Blood Pressure Chart: Normal, High & Low BP Readings
Author: Ian C. Langtree - Writer/Editor for Disabled World (DW)
Published: 2017/11/19 - Updated: 2026/01/16
Publication Type: Charts, Graphs, Tables
Category Topic: Calculators - Charts - Related Publications
Page Content: Synopsis - Introduction - Main - Insights, Updates
Synopsis: This information provides a clinical reference guide for interpreting cardiovascular health metrics across different age groups and risk categories. The resource proves particularly valuable for older adults, individuals with mobility limitations, and those managing chronic conditions who need accessible tools to track their health markers at home. By presenting blood pressure classifications from normal ranges through various stages of hypertension, including age-specific guidelines and measurement techniques, the chart enables users to recognize when readings fall outside healthy parameters. The information draws from American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology standards, making it authoritative for anyone monitoring cardiovascular risk factors, especially important for populations at higher risk of heart disease and stroke - Disabled World (DW).
- Definition: Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the measurement of the pressure of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. Arteries carry blood from your heart to other parts of your body. The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association divides blood pressure into four general categories. Ideal blood pressure is categorized as normal. Increased blood pressure may be classified as elevated, stage 1, or stage 2, depending on the specific numbers. High blood pressure (hypertension) can be dangerous if not treated. It can put you at risk for stroke, heart failure, kidney failure, and other medical problems.
Introduction
NOTE: High blood pressure often does not cause any signs of illness that you can see or feel. It is important to make an appointment with your doctor or another healthcare provider to check your blood pressure.
Main Content
What Does Blood Pressure Refer To?
Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels and constitutes one of the body's principal vital signs. The pressure of the circulating blood decreases as blood moves through your arteries, arterioles, capillaries, and veins. The term blood pressure generally refers to your arterial pressure, i.e., the pressure in the larger arteries, arteries being the blood vessels that take blood away from the heart. Blood pressure is always given as two numbers;
- Systolic Pressure (when the heart beats)
- Diastolic Pressure (when the heart relaxes)
When the measurements are written, both are written as one above or before, the other with the systolic being the first number, for example, 120/75 (120 over 75). Blood pressure measurement is NOT the same as your heart rate (pulse) or maximum heart rate measurement. Check what your heart rate for your age should be. You can calculate your predicted maximum heart rate by using the calculation: 220 - (age) = Age Predicted Maximum Heart Rate - or see our Target Heart Rate Calculator and Chart.
Measuring Your Blood Pressure
Healthcare professionals use a stethoscope and a manual sphygmomanometer to measure your blood pressure. Typically, they take the reading above your elbow. The sphygmomanometer has a bladder, cuff, bulb, and gauge. When the bulb is pumped, it inflates the bladder inside the cuff wrapped around your arm. This inflation will stop the blood flow in your arteries.
The stethoscope is used to listen for the sound of the heartbeat, and no sound indicates no flow. As the pressure is released from the bladder, you will hear the blood flowing again. That point becomes reading your blood pressure systolic. The diastolic reading is when you hear no sound again, which means the blood flow is back to normal.
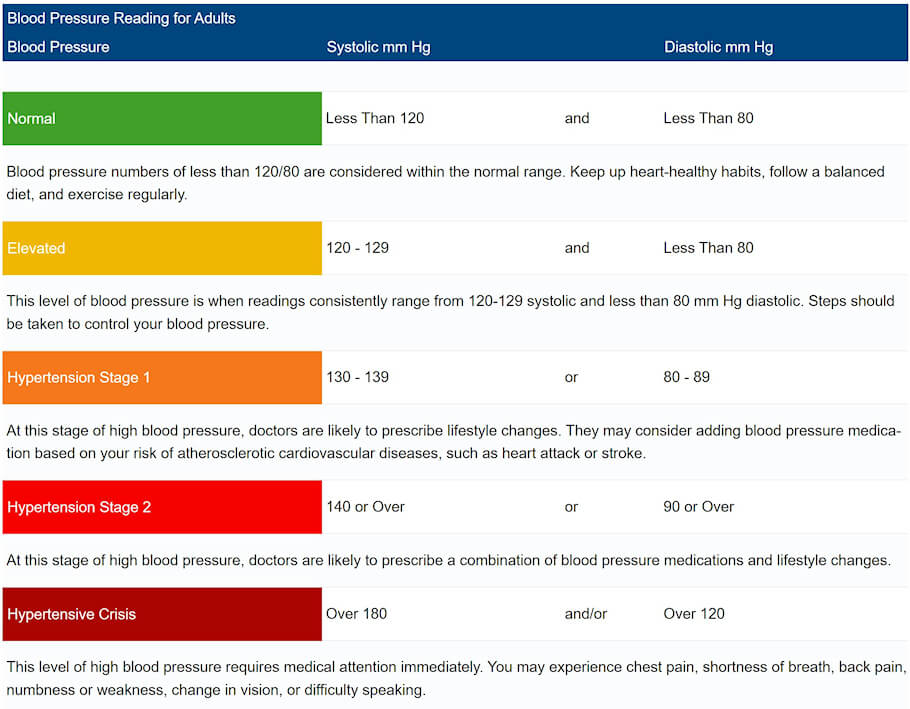
Blood Pressure Chart For Adults
| Blood Pressure | Systolic mm Hg | Diastolic mm Hg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Less Than 120 | and | Less Than 80 |
| Blood pressure numbers of less than 120/80 are considered within the normal range. Keep up heart-healthy habits, follow a balanced diet, and exercise regularly. | |||
| Elevated | 120 - 129 | and | Less Than 80 |
| This level of blood pressure is when readings consistently range from 120-129 systolic and less than 80 mm Hg diastolic. Steps should be taken to control your blood pressure. | |||
| Hypertension Stage 1 | 130 - 139 | or | 80 - 89 |
| At this stage of high blood pressure, doctors are likely to prescribe lifestyle changes. They may consider adding blood pressure medication based on your risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack or stroke. | |||
| Hypertension Stage 2 | 140 or Over | or | 90 or Over |
| At this stage of high blood pressure, doctors are likely to prescribe a combination of blood pressure medications and lifestyle changes. | |||
| Hypertensive Crisis | Over 180 | and/or | Over 120 |
| This level of high blood pressure requires medical attention immediately. You may experience chest pain, shortness of breath, back pain, numbness or weakness, change in vision, or difficulty speaking. | |||
| Normal, healthy, and unhealthy blood pressure ranges as recommended by the American Heart Association. | |||
Blood Pressure Chart By Age
Creating a comprehensive blood pressure chart by age involves several factors, including gender and health status. However, here's a general guideline for blood pressure ranges by age for adults:
| Age Group | Systolic BP (mm Hg) | Diastolic BP (mm Hg) |
|---|---|---|
| 18-29 | 120-129 | 80-84 |
| 30-39 | 120-129 | 80-84 |
| 40-49 | 130-139 | 85-89 |
| 50-59 | 130-139 | 85-89 |
| 60+ | 140 or higher | 90 or higher |
NOTE: These ranges are based on guidelines from organizations like the American Heart Association. However, individual health conditions and other factors may influence what's considered a normal range for blood pressure. A healthcare provider recommends you get your blood pressure checked at least once a year. If you have been diagnosed with high blood pressure (or other related conditions), your doctor may recommend getting it checked more often.
Human Blood Pressure Facts
- The general pattern is that blood pressure rises with age, so normal variations are higher for older adults.
- Blood pressure can be higher in obese people because the heart has to work harder to perfuse the body's tissues.
- Factors that influence blood pressure include age, sex, ethnicity, weight, exercise, emotions/stress, pregnancy, and diurnal rhythm, as well as medication use and disease processes.
- Blood pressure is similar in childhood for males and females. After puberty, females have a lower blood pressure than males, whereas, after menopause, females have a higher blood pressure than males.
- The sympathetic nervous system is stimulated by exercise, stress, anxiety, pain, anger, and fear, which increases blood pressure. Blood pressure returns to baseline within five minutes of rest following activity.
- The diurnal cycle influences blood pressure to be lower in the morning and increase throughout the day until early evening. This is one reason healthcare providers document the time a client's blood pressure is taken.
- Research has revealed that ethnicity may be a predictor of blood pressure, but this causation is not necessarily biological but rather sociocultural. When determining the risk for high blood pressure, it is important to consider ethnicity as a contributing factor.
- Blood pressure varies throughout the duration of pregnancy. It decreases about halfway through the first trimester until mid-pregnancy due to progesterone effects that relax the walls of blood vessels, causing decreased peripheral vascular resistance. It returns to pre-pregnancy values toward the end of pregnancy.
Printable High, Low, Normal Blood Pressure Chart
Nearly half, over 119 million, American adults have high blood pressure. But only about 1 in 4 of those people have their condition under control. Many people develop high blood pressure when they are in their late 30's or early 40's, and it occurs more frequently as people age. However, because of the obesity epidemic, more and more children are also developing high blood pressure - fda.gov
Insights, Analysis, and Developments
Editorial Note: Regular blood pressure monitoring remains one of the most straightforward yet powerful tools for protecting long-term health. What makes this particularly relevant today is how cardiovascular risk factors often develop silently over years, making periodic checks essential rather than optional. For people managing disabilities or age-related health changes, understanding these numbers means gaining practical knowledge about when to seek medical guidance and when readings reflect healthy baselines. The real value isn't just in the numbers themselves, but in recognizing patterns over time and knowing which lifestyle modifications or medical interventions might help maintain readings within target ranges for your specific age and health profile - Disabled World (DW). Author Credentials: Ian is the founder and Editor-in-Chief of Disabled World, a leading resource for news and information on disability issues. With a global perspective shaped by years of travel and lived experience, Ian is a committed proponent of the Social Model of Disability-a transformative framework developed by disabled activists in the 1970s that emphasizes dismantling societal barriers rather than focusing solely on individual impairments. His work reflects a deep commitment to disability rights, accessibility, and social inclusion. To learn more about Ian's background, expertise, and accomplishments, visit his full biography.
Author Credentials: Ian is the founder and Editor-in-Chief of Disabled World, a leading resource for news and information on disability issues. With a global perspective shaped by years of travel and lived experience, Ian is a committed proponent of the Social Model of Disability-a transformative framework developed by disabled activists in the 1970s that emphasizes dismantling societal barriers rather than focusing solely on individual impairments. His work reflects a deep commitment to disability rights, accessibility, and social inclusion. To learn more about Ian's background, expertise, and accomplishments, visit his full biography.