Endogenous Retrovirus Activation Increases Fetus Autism Susceptibility
Author: Kobe University
Published: 2023/03/10 - Updated: 2024/08/03
Publication Details: Peer-Reviewed, Findings
Category Topic: Autism Information - Academic Publications
Page Content: Synopsis - Introduction - Main
Synopsis: Ancient virus genome drives autism revealed as discoveries regarding autism onset found in research models. They also discovered that BTBR/R exhibits autistic-like behaviors without reduced learning ability, making it a more accurate model of autism than the widely-used BTBR/J model.
Defining Human Endogenous Retroviruses (HERVs)
- Human Endogenous Retroviruses (HERVs)
Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) are a family of viruses within our genome with similarities to present-day exogenous retroviruses. Successive generations have inherited HERVs, and some may have conferred biological benefits. Human endogenous retroviruses represent footprints of previous retroviral infection and have been termed "fossil viruses." They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, comprising up to 5-8% of the human genome (lower estimates of ~1%).
Introduction
Although autism is a common neurodevelopmental disorder, the multiple factors behind its onset are still not fully understood. Animal models of idiopathic autism(1), especially mice, are often used to help researchers understand the complicated mechanisms behind the disorder, with BTBR/J being the most commonly used mouse model globally.
Main Content
Now, an international research collaboration including Kobe University's Professor TAKUMI Toru and Researcher Chia-wen Lin et al. have made discoveries regarding autism onset in mouse models.
In their detailed series of experiments and analyses of BTBR/J mice and the other subspecies BTBR/R, they revealed that endogenous retrovirus(2) activation increases a fetus's susceptibility to autism. They also discovered that BTBR/R exhibits autistic-like behaviors without reduced learning ability, making it a more accurate model of autism than the widely-used BTBR/J model.
It is hoped that further research will contribute towards the better classification of autism types and the creation of new treatment strategies for neurodevelopmental disorders(3).
These research results was published in Molecular Psychiatry on March 7, 2023,
Main Points
- The researchers analyzed BTBR/J(4), a widely used mouse model of autism, and its subspecies BTBR/R(5) using MRI(6). This revealed that the corpus callosum(7), which connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, was impaired in BTBR/J mice but not in BTBR/R mice.
- Genome and transcription analysis showed that BTBR mice have increased levels of endogenous retrovirus genes.
- Furthermore, single-cell RNA analysis(8) of BTBR/R mice revealed changes in the expression of various genes (including stress response genes) indicative of endogenous retrovirus activation.
- Even though BTBR/J and BTBR/R mice have the same ancestry, the results of various behavioral analysis experiments revealed differences in spatial learning ability and other behaviors between the two types of model mice.
Research Background
Autism (Autism Spectrum Disorder) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that remains largely unexplored despite the rapidly increasing number of patients. Reasons for this continuing increase in people diagnosed with autism include changes to diagnostic criteria and older fathers becoming more common. Autism is strongly related to genetic factors and can be caused by abnormalities in DNA structure, such as copy number variations(9).
Animal models, especially mice, are often used in research to illuminate the pathology of autism. Among these models, BTBR/J is a mouse model of the natural onset of autism that is commonly used. Studies have reported various abnormalities in BTBR/J mice, including impairment of the corpus callosum (which connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain) and excessive immune system signaling. However, why this lineage displays autistic-like behavioral abnormalities is not fully understood.
the current study aimed to shed light on the onset mechanism of these autistic-like behavioral abnormalities by conducting a comparative analysis on BTBR/J and its subspecies BTBR/R.
Research Findings
First, the researchers conducted MRI scans on BTBR/J and BTBR/R mice to investigate structural differences in each brain region. The results revealed differences between BTBR/J and BTBR/R mice in 33 regions, including the amygdala. A particularly prominent difference discovered was that even though BTBR/J's corpus callosum is impaired, BTBR/R's is normal (Figure 1).

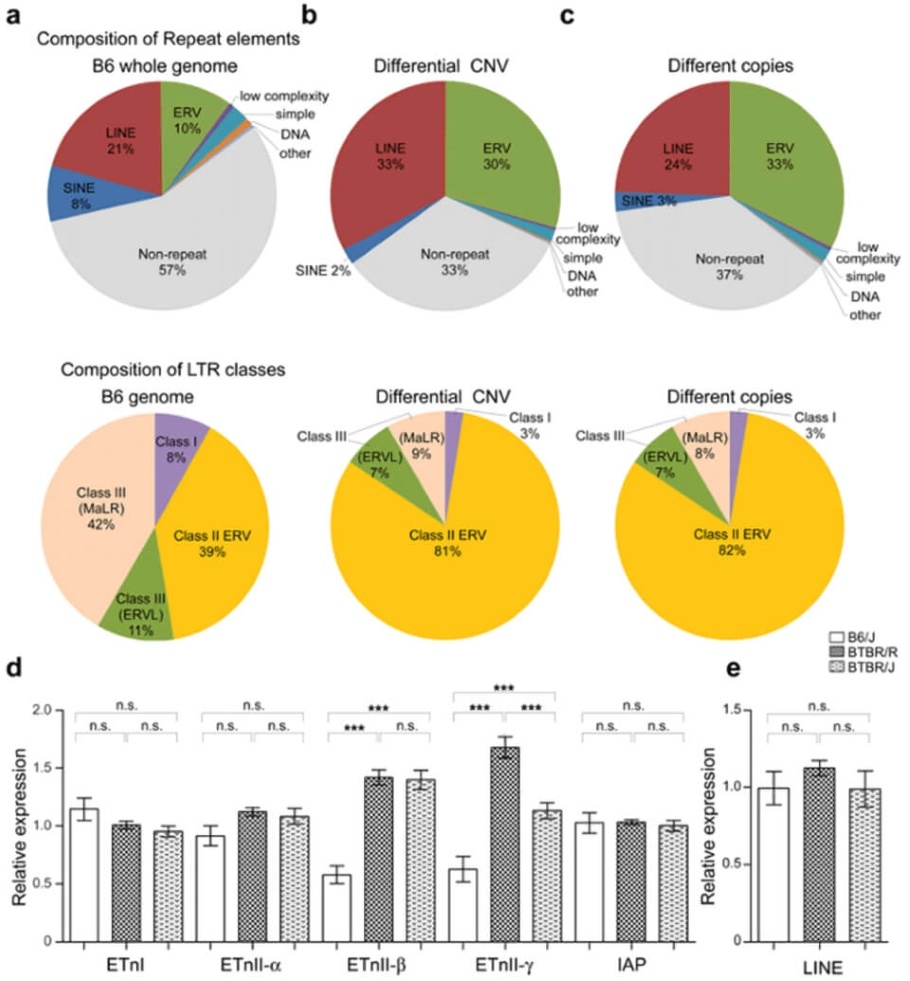
Next, the research group used the array CGH method(10) to compare BTBR/R's copy number variations with a normal mouse model (B6). They revealed that BTBR/R mice had significantly increased levels of endogenous retroviruses (ERV) compared to B6 mice (Figure 2 a-c). Furthermore, qRT-PCR tests revealed that these retroviruses were activated in BTBR/R mice (Figure 2d). On the other hand, in B6 mice, there was no change in the expression of LINE ERV (which is classified in the same repetitive sequence), indicating that this retroviral activation is specific to BTBR (Figure 2e).
Subsequently, the researchers carried out single-cell RNA analysis on the tissue of embryonic BTBR mice (on the AGM(11) and yolk sac(12). The results provide evidence of ERV activation in BTBR mice, as expression changes were observed in a group of genes downstream of ERV (Figure 3).

Lastly, the researchers comprehensively investigated the differences between BTBR/J and BTBR/R on a behavioral level. BTBR/R mice were less anxious than BTBR/J and showed qualitative changes in ultrasound vocalizations, which are measured as a way to assess communicative ability in mice (Figure 4a-f). BTBR/R mice also exhibited more self-grooming behaviors and buried more marbles in the marble burying test (Figure 4g, h). These two tests were designed to detect repetitive behavioral abnormalities in autistic individuals. From the results, it was clear that BTBR/R exhibits more repetitive behaviors (i.e., it is more symptomatic) than BTBR/J. The 3-chamber social interaction test*13, which measures how closely a mouse will approach another mouse, also revealed more pronounced social deficits in BTBR/R than in BTBR/J mice (Figure 4i). In addition, a Barnes maze was used to conduct a spatial learning test, in which BTBR/J mice exhibited reduced learning ability compared to B6 (normal mice). BTBR/R mice, on the other hand, exhibited a similar ability to B6 (Figure 4j).

Overall, the study revealed that retrovirus activation causes the copy number variants in BTBR mice to increase, which leads to the differences in behavior and brain structure seen in BTBR/J and BTBR/R mice (Figure 5).

Further Developments
BTBR/J mice are widely used by researchers as a mouse model for autism. However, the results of this study highlight the usefulness of the other lineage of BTBR/R mice because they exhibit autistic-like behavior without compromised spatial learning ability. The results also suggest that it may be possible to develop new treatments for autism that suppress ERV activation. Furthermore, it is necessary to classify autism subtypes according to their onset mechanism, which is a vital first step toward opening up new avenues of treatment for autism.
Glossary
1. Idiopathic autism: Autism is considered to be a multifactorial disorder that genetic and environmental factors can cause. It is understood that genetic factors such as genetic and genomic abnormalities can cause autism. However, there are still many cases of autism where the cause is unknown. Autism, where the cause (including environmental factors) cannot be specified, is called idiopathic autism.
2. Endogenous retrovirus: A general term for an RNA virus with reverse transcription. Most of these viruses are ancient and inactive and have been passed down through species over generations. About 8% of the human genome consists of these retroviruses.
3. Neurodevelopmental disorder: Previously called a developmental disorder, this disorder occurs as a functional problem with the brain.
4. BTBR/J: A type of congenic mouse. Systemic behavior analyses of the BTBR line of mice have shown that it is the line that most closely resembles autistic behavior. Therefore, it is known as the idiopathic autism mouse model. Jackson Laboratory (USA) maintains and preserves this line, widely used in autism research.
5. BTBR/R: This line of autism model mice has the same origin as BTBR/J. It was deposited at Riken Bioresource Research Center (Japan) in 1987 and has been maintained and preserved by the center ever since.
6. MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging. A non-invasive method that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to generate various cross-sectional images of the brain and other organs.
7. Corpus callosum: A bundle of commissural fibers. Commissural fibers connect the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
8. Single-cell RNA-seq: A method of comprehensively investigating the qualitative and quantitative aspects of all mRNA present in individual cells using a next-generation sequencer. Combining this with statistical analysis methods such as dimension reduction makes classifying cells based on their genetic expression and estimating the cell state possible. Furthermore, performing pseudo-temporal ordering analysis based on changes in the gene expression profile makes it possible to depict fibers in the cellular state accompanying development.
9. Copy number variation: A copy number variation (polymorphism) is a phenomenon in which there is either less than one copy (deletion) or more than three copies (duplication) of genomic DNA that spans more than one kilobase (kb) on a chromosome. Normally there should be two copies. This is a copy number variation if there are three or just one copy. Copy number variations are found in 12% of the human genome. Copy number variations can exist in healthy, normal genomes and cause genomic disease.
10. Array CGH method: This method can detect genome abnormalities, including genomic DNA amplification and defects, on a high-resolution scale encompassing all the chromosomes.
11. AGM: The Aorta-gonad-mesonephros (AGM) region is a hematopoietic site within the fetus (i.e., where cellular components of the fetus's blood are formed).
12. Yolk sac (YS): The yolk sac performs many critical functions that enable a fetus to develop; for example, it is involved in blood cell production (primary hematopoiesis).
13. 3-chamber social interaction test: An experiment to evaluate a mouse's sociability. Normally, mice are strongly interested in other mice. Therefore, they spend more time in the chamber where there is another mouse than in the empty chamber.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by funding from organizations including the following:
- Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
- The Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development's 'Strategic Research Program for Brain Sciences (SRPBS)' (Psychiatric & Neurological Disorders)
- Takeda Science Foundation
Journal Information
Title:
"An old model with new insights: endogenous retroviruses drive the evolvement toward ASD susceptibility and hijack transcription machinery during development"
Authors:
Chia-Wen Lin(1,2,3), Jacob Ellegood(4), Kota Tamada(1,3), Ikuo Miura(5), Mikiko Konda(6), Kozue Takeshita(6), Koji Atarashi(6,7), Jason P Lerch(4,8), Shigeharu Wakana(5), Thomas J. McHugh(2) and Toru Takumi(1,3,9).
- 1 Laboratory for Mental Biology, RIKEN Brain Science Institute; Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan.
- 2 Laboratory for Circuit and Behavioral Physiology, RIKEN Center for Brain Science; Wako, Saitama 351-0198, Japan.
- 3 Department of Physiology and Cell Biology, Kobe University School of Medicine, Chuo, Kobe 650-0017, Japan.
- 4 Mouse Imaging Centre, Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario M5T 3H7, Canada.
- 5 Technology and Development Team for Mouse Phenotype Analysis, Japan Mouse Clinic, RIKEN BioResource Research Center, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0074, Japan
- 6 Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Keio University School of Medicine; Shinjuku, Tokyo 160-8582, Japan
- 7 RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences, Tsurumi, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan.
- 8 Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging, University of Oxford, Oxford, Oxfordshire OX39DU, UK
- 9 RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research, Chuo, Kobe 650-0047, Japan.
(*) Corresponding author
Journal:
Molecular Psychiatry
Attribution/Source(s): This peer reviewed publication was selected for publishing by the editors of Disabled World (DW) due to its relevance to the disability community. Originally authored by Kobe University and published on 2023/03/10, this content may have been edited for style, clarity, or brevity.